Choosing the Right Track to Cut Post-Harvest Losses

Choosing the Right Track to Cut Post-Harvest Losses
Syllabus: GS3/Agriculture
Context
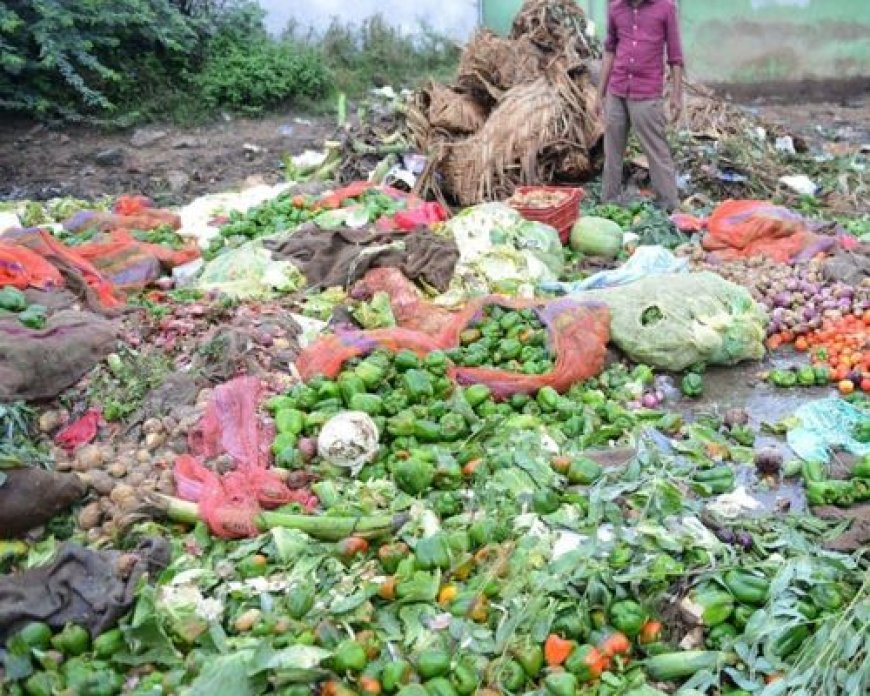
Post-harvest losses continue to be a significant challenge for the agricultural sector in India, affecting the livelihoods of farmers and contributing to food insecurity. Addressing these issues is crucial to ensuring food security and improving the economic conditions of farmers.
The Importance of Post-Harvest Management
Post-harvest management involves a series of activities such as cleaning, sorting, drying, storing, processing, packaging, and transporting agricultural produce. Effective management in these areas can significantly reduce the wastage of food, ensuring that a larger proportion of the harvest reaches consumers in good condition. The economic benefits include increased income for farmers, reduced prices for consumers, and lower dependency on imports.
Key Strategies to Reduce Post-Harvest Losses
1. Improved Storage Facilities:
o Modern Warehouses: Building modern warehouses with climate control can help in preserving the quality of produce. These facilities can reduce spoilage caused by extreme temperatures and humidity.
o Cold Storage: For perishable items like fruits and vegetables, cold storage facilities are essential. These can extend the shelf life of produce, allowing farmers to sell their products at better prices and reduce wastage.
2. Efficient Supply Chains:
o Logistics Optimization: Streamlining transportation and logistics can ensure quicker and safer delivery of produce from farms to markets. Implementing technologies like GPS tracking and route optimization can minimize delays and spoilage.
o Aggregation Centers: Establishing aggregation centers where farmers can bring their produce for sorting, grading, and packing before it is sent to markets can improve efficiency and reduce losses.
3. Technology and Innovation:
o Digital Platforms: Using digital platforms for market linkages can help farmers find buyers quickly, reducing the time produce spends in transit and storage. Apps and online marketplaces can facilitate direct sales from farmers to consumers.
o Processing Units: Setting up processing units close to farming areas can add value to agricultural produce. This includes activities like canning, freezing, drying, and packaging, which can reduce losses and provide additional income streams for farmers.
4. Training and Capacity Building:
o Farmer Education: Educating farmers on best practices for post-harvest handling, including proper harvesting techniques and the use of appropriate tools, can reduce damage to produce.
o Extension Services: Strengthening agricultural extension services to provide ongoing support and advice to farmers on post-harvest management can ensure the adoption of best practices.
5. Policy Support:
o Government Schemes: The government can introduce and expand schemes that provide financial assistance for building storage infrastructure and purchasing equipment for post-harvest management.
o Regulatory Framework: Developing a robust regulatory framework to ensure quality standards in post-harvest processes can encourage investments in this sector and improve overall efficiency.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Several states in India have successfully implemented initiatives to reduce post-harvest losses. For example:
- Maharashtra: The state has invested in cold storage facilities and pack houses, significantly reducing losses in the horticulture sector.
- Punjab: The establishment of modern grain storage silos has helped in preserving the quality of grains, reducing losses during storage and transportation.
Conclusion
Reducing post-harvest losses is critical for enhancing food security, improving farmer incomes, and ensuring sustainable agricultural practices. By adopting a combination of improved storage facilities, efficient supply chains, technology, farmer education, and supportive policies, India can significantly reduce these losses. Collaboration between government, private sector, and farmers is essential to create a resilient agricultural system that minimizes waste and maximizes the value of the harvest.
What's Your Reaction?