Assam’s Charaideo Maidam Added to UNESCO World Heritage List

Assam’s Charaideo Maidam Added to UNESCO World Heritage List
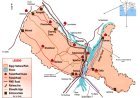
The Charaideo Maidam, an ancient burial mound site associated with the Ahom dynasty in Assam, has been added to the UNESCO World Heritage list under the Cultural Property category. This marks the first time a site from Northeast India has been included in this list.
The Charaideo Maidams feature pyramid-like structures known as "Moidams," which serve as burial sites for Ahom rulers. Out of 386 maidams explored so far, 90 royal burials at Charaideo are the best-preserved examples of this tradition. The site has gained recognition for its cultural and historical significance.
What are Moidams?
- Description: The Moidams represent the late medieval (13th-19th century CE) mound burial tradition of the Tai Ahom Dynasty of Assam.
- Construction: These were primarily constructed using earth, bricks, and stone. The outer structure typically consisted of a mound of earth, often surrounded by a brick or stone wall.
- Location: They are the resting place of royal families in Assam’s Charaideo district.
- Contents: The Moidams enshrine the mortal remains of the members of the Ahom royalty, who used to be buried with their paraphernalia.
- Cultural Shift: After the 18th century, the Ahom rulers adopted the Hindu cremation method and began entombing the cremated bones and ashes in a Maidam at Charaideo.
- Comparison: These burial systems of the Ahom dynasty are comparable to the royal tombs of ancient China and the Pyramids of the Egyptian Pharaohs.
What are the Key Facts About the Ahom Kingdom?
- Establishment: The Ahom kingdom was established in 1228 in Assam's Brahmaputra valley and maintained its sovereignty for 600 years. It was founded by the 13th-century ruler Chaolung Sukapha in 1253.
- Capital: Charaideo was their initial capital, located over 400 km east of Guwahati.
- Duration: The Ahom dynasty ruled for approximately 600 years until Assam was annexed by the British in 1826 through the Treaty of Yandaboo.
Political Setup
- State Formation: Ahoms created a new state by suppressing the older political system of the bhuiyans (landlords).
- Labor System: The state depended upon forced labour, known as paiks.
Society
- Structure: Ahom society was divided into clans or khels. A khel often controlled several villages.
- Religion and Language: Ahoms worshipped their own tribal gods, yet they accepted the Hindu religion and the Assamese language. However, the Ahom kings did not completely give up their traditional beliefs after adopting Hinduism.
Military Strategy
- Composition: The full contingent of the Ahom Army consisted of infantry, navy, artillery, elephantry, cavalry, and spies.
- Weapons: The main war weapons consisted of bows and arrows, swords, javelins, discus, guns, matchlocks, and cannons.
- Tactics: The Ahom soldiers were experts in guerrilla fighting. They also learned the technique of constructing boat bridges in the Brahmaputra.
- Historical Victory: The Ahom navy, led by Lachit Borphukan, defeated the Mughal forces commanded by Ram Singh I during the reign of Aurangzeb at the Battle of Saraighat in 1671. The Lachit Borphukan gold medal is awarded to the best cadet from the National Defence Academy. The medal was instituted in 1999 to inspire defence personnel to emulate Borphukan’s heroism and sacrifices.
What's Your Reaction?